Table of Contents:
- What is FMEA?
- Why is FMEA important?
- When is FMEA necessary?
- How the FMEA process works.
- Digitizing the FMEA process
- Conclusion
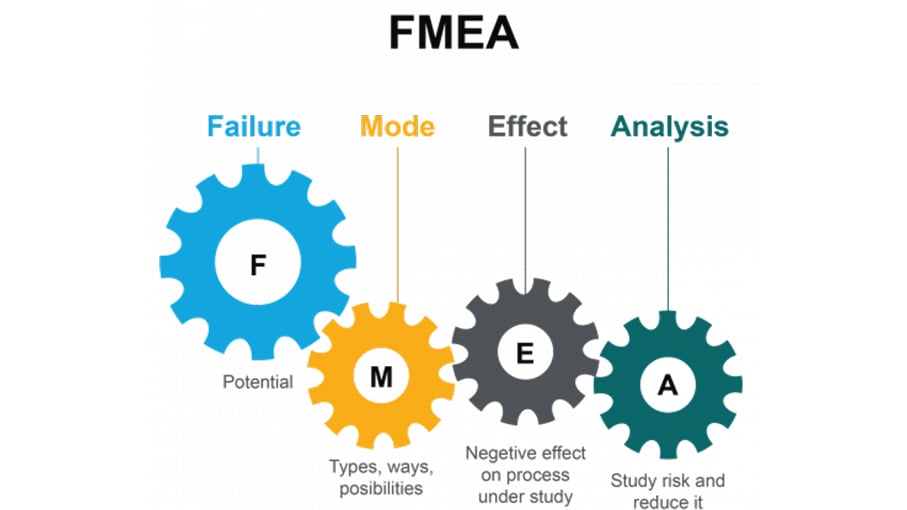
What is FMEA?
Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) is a systematic method of identifying and preventing potential failures in a product or process before they occur. It involves analyzing the potential failure modes, their effects, and the likelihood of occurrence and severity of each failure mode. FMEA is used to identify potential risks and take proactive measures to reduce or eliminate them.
Why is FMEA important?
FMEA is important because it helps companies to identify and mitigate potential risks before they occur, reducing the likelihood of costly failures and improving overall product quality. It can also help companies to meet regulatory requirements and improve customer satisfaction by delivering products that meet or exceed expectations.
When is FMEA necessary?
FMEA is necessary in any situation where failure can have serious consequences, such as in medical devices, aerospace, and automotive industries. It is also useful in any situation where quality and reliability are critical to the success of the product, such as in manufacturing, software development, and engineering.
How the FMEA process works.
The FMEA process involves the following steps:
- Identify the system, product or process to be analyzed.
- Identify potential failure modes and their effects.
- Assign a severity ranking to each potential failure mode.
- Identify the potential causes of each failure mode.
- Assign a likelihood ranking to each potential cause.
- Identify existing controls and assign a ranking to each control.
- Determine the risk priority number (RPN) for each failure mode by multiplying the severity, likelihood, and detectability rankings.
- Develop and implement corrective actions to reduce or eliminate the highest RPNs.
- Monitor the effectiveness of the corrective actions and revise the FMEA as necessary.
Digitizing the FMEA process
Digitizing the FMEA process can improve its efficiency and effectiveness by reducing the time and effort required to conduct an analysis, improving collaboration among team members, and providing real-time data for decision-making. There are several software tools available for digitizing the FMEA process, such as Excel-based templates, cloud-based tools, and dedicated FMEA software.
Conclusion
FMEA is a powerful tool for identifying and mitigating potential risks in a product or process. By systematically analyzing potential failure modes and their effects, companies can take proactive measures to reduce or eliminate risks and improve overall product quality. With the availability of digitized FMEA tools, companies can streamline the process and improve collaboration among team members, leading to better decision-making and improved outcomes.
Understanding Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) and Its Importance in Product Development
by u/rmgyoutube in u/rmgyoutube
FAQs about FMEA
FMEA stands for Failure Mode and Effects Analysis.
The purpose of FMEA is to identify and mitigate potential failures in a product or process before they occur.
FMEA is commonly used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, medical devices, manufacturing, software development, and engineering.
The benefits of FMEA include reducing the likelihood of costly failures, improving product quality, meeting regulatory requirements, and improving customer satisfaction.
The FMEA process involves identifying potential failure modes, assigning severity and likelihood rankings, identifying potential causes and controls, determining the risk priority number (RPN) for each failure mode, developing and implementing corrective actions, and monitoring the effectiveness of the corrective actions.






0 Comments